Introduction
Types of cloud computing – computing is a way to access info and requests online instead Cloud of creating, managing and maintaining them on your hard drive or servers. It is fast, efficient and safe. It is also a bit slippery. Although most of us have been using the cloud for years, the inquiry still resonates within many organizations: what is cloud computing?
Whether you want to understand it better or are trying to help your organization use it more effectively, this guide can help.
What is Cloud Computing?
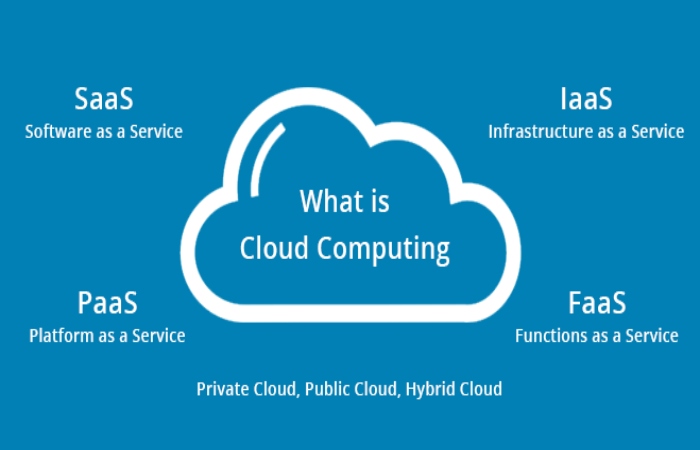
Simply put, cloud computing is a way to access services over the Internet rather than on your computer. You can use the cloud to access apps, data, and developer tools from virtually anywhere. Whether working on your phone from a crowded train in Chicago or on your laptop in a hotel in Hong Kong, you can access the same information because everything is online.
Who uses Cloud Computing?
The short answer is everyone. The cloud is everywhere, from your phone and car to your smartwatch and your favorite grocery delivery app.
But cloud computing is compelling for businesses. Because it gives them to give and scalability, organizations of all sizes and industries are already using cloud computing. Enterprises use it for routine tasks such as data protection, software development, data analysis, disaster recovery, virtual desktops, server virtualization, and customer-facing applications.
How Does Cloud Computing Work?
Simply put, cloud computing is a puzzle made up of three essential bits:
Cloud-ability workers stock facts and applications on bodily machines in locations called data centres.
Users access these assets. Types of Cloud Computing
The Internet instantly connects providers and users over long distances.
Although the parts are simple, the technology that puts them together is complex. To appreciate this, consider how things worked before the cloud: corporate IT teams ran their own on-premises data centres, which required regular hardware upgrades, bloated electricity bills, and excessive amounts of real estate. It was expensive, inconvenient and inefficient. Types of Cloud Computing
But this is no longer necessary. Companies that previously operated their data centres no longer have to worry about provisioning, protecting, scaling, maintaining, and updating infrastructure. They focus solely on creating exceptional customer experiences instead of technical logistics. It radically changes and simplifies the way businesses approach their IT resources.
For example, many cloud providers offer subscription services. Customers can contact all the computing resources they need for a monthly subscription. It means they don’t have to buy software licenses, upgrade outdated servers, buy more machines when they run out of storage, or install software updates to keep up with evolving security threats. Instead, the seller does all of this for them.
In this way, cloud computing is like renting a car. The user can drive the vehicle, but it is up to the owner to perform routine repairs and maintenance and replace old vehicles with new ones as they age. And if the user ever wants an upgrade to house more business, it’s as simple as passing a new lease and exchanging keys.
Examples of Cloud Computing at Home and Work
As technology advances, cloud computing is becoming more and more common. And it completely transforms modern life in the process, both at home and at work.
CC at home
In your personal life, you are probably using cloud computing without even grasping it. Instead of storing detailed reproductions of movies and music in cabinets or on shelves, you can now access them virtually through cloud-based streaming services like Netflix and Spotify. What about the photos and comments you post on social media? Social networks like Facebook and Twitter also store them remotely in the cloud.
Cloud computing at work
You secondhand store files on your firm drive at work and often lose them during organization crashes and power failures. Now you’re probably storing them in the cloud, which saves your changes in real-time so you can access them anywhere.
Your organization can also use cloud-based customer relationship management (CRM) software, making it easy to personalize customer communications, manage leads, and adjust marketing efforts across departments. Or, you can use cloud-based solutions for HR, payroll, accounting, and logistics. In these business use cases and countless others, cloud computing can facilitate enhanced security and simplified data entry, not to mention time-saving automation.


